Composite Layup Process
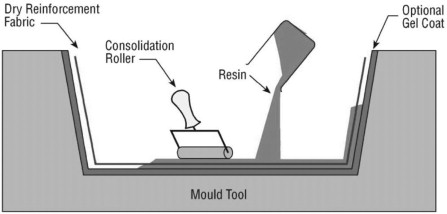
Hand layup method is the oldest FRP molding method for making FRP GRP composite products. It does not require technical skills and machinery. It’s a way of small volume and high labor intensity, especially suitable for large parts such as FRP vessel. Half of the mold is usually used during composite layup process. The figure below shows the typical structure of the hand layup composite.
The mold have the structural shapes of the FRP products. In order to make the product surface shiny or textured, the mold surface should have a corresponding surface finish. If the outer surface of the product is smooth, the product is made inside the female mold. Likewise, if the inside must be smooth, then molding is done on the male mold. The mold should be free of defects because the FRP product will form the mark of the corresponding defect.
Because the resin used is highly viscous, the product may stick to the mold. There should be a suitable release mechanism. Product release may be affected. By using the layer of wax or polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), or a thin film like polyester film (Mylar). Composite layup process is not suitable for complex structural shapes because Mylar sheets must fit into the mold GRP profiles.
Hand Lay Up Method
- Gel coat
Gel coat gives you the smoothness required for the fiberglass product. It is usually a thin layer of resin that is about several mm on the surface of the product. Adding proper pigments to the resin, and then the color is obtained. The gel coat forms a protective layer to protect the fiberglass from contacting with water and chemicals. If it is too thin, the fiber pattern will become visible. If it is too thick, there will be crazing and star cracks on the tape.
- Surface mat layer
The surface mat layer will be placed under the gel coat. The fiber of the mat is not as strong as the reinforced fiber, but the mat provides the anti-crack and impact strength for the rich resin layer. This is an optional layer that is only used in a particular situation.
- Glass fiber laminate
The resin wetted glass fiber layer shall be laid in sequence until the required thickness is reached. The finished material is called a lamination. Laminate gives the fiberglass product strength and rigidity. Glass fibers in the chopped strand mat (CSM) are usually used for obtaining composite material products. Woven roving, one-way mat and two-way mat are also used for acquiring high strength composite materials.
- Surface mat layer/resin coating
Fiberglass laminate provides a rough surface finish. In order to obtain a smoother surface, we can apply a surface mat or resin coating to the laminate and smooth it by placing a thin layer of Mylar.
Advantages:
This is a low-volume, labor-intensive method. It’s suitable for many fiberglass reinforced plastic products, such as FRP vessel, fiberglass car bodies, FRP pipe, FRP tank, furniture, corrosion resistant FRP equipment. No expensive machinery is necessary. Almost all shapes and sizes can be made. The color and texture can be obtained through the hand layup method. Choosing composite layup process as a FRP process. As a GRP manufacturing method, the following conditions are good for hand lay up. Only one side needs to have a smooth surface. The product has large size and complex shape. Only a small amount of components are needed.
Limitations:
The quality of the FRP product depends on the operator’s skill. Not suitable for mass fiber glass production of high-speed small products. It is hard to obtain a free-space composite material.
About The Moulds:
The opening process of FRP manufacturing uses a male or female mold. The moulds can be finished by using Paris, wood, fiberglass or metal as material in hand lay up method. Paris mold gypsum is one or at most two, because the mold may break during the release of the fiberglass product. Wood modules need to be completed at each molding cycle. The glass steel mould is the ideal choice for complex shape. Metal molds are preferred when heating and pressing are needed.